At the start of each year we ask the EcoEvo contributors to share their favourite scientific publications from the past year and why they found them interesting, inspiring, or otherwise worthy of inclusion in the Hall of Fame. Keeping with tradition, here are the EcoEvo Hall of Fame entries for 2020! And if you enjoy reading about our favourite papers from 2020, remember you can also check out our favourites from 2017, 2018 and 2019, too!

Chosen by Andrew Neill
Read the full People and Nature paper here.
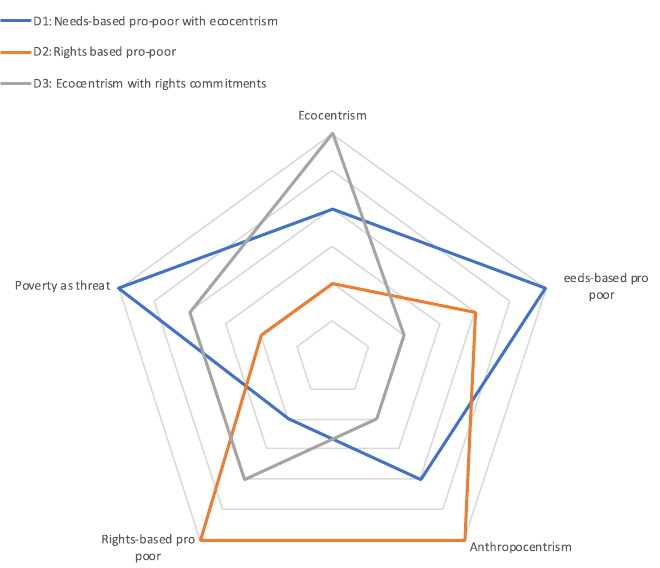
I really enjoyed this paper because it tackles a really difficult topic at the intersection of poverty, human rights, development, conservation, and sustainability. It is important to remember that conservation will never meet its objectives without considering how people depend on nature for their needs and livelihoods. The areas of richest biological diversity (and therefore conservation potential) are usually in developing countries with communities experiencing poverty. This paper collects responses from conservation practitioners to examine their viewpoints on poverty in the context of their work.
© 2020 The Authors. People and Nature published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Ecological Society. The article is distributed under the terms of the CC-BY 4 license.
They found some areas of agreement such as the poorest people should not be expected to shoulder the costs of preserving a global public good (the conservation of biodiversity). However, they also identify differences between responses: Is the focus placed on meeting the needs of people or more closely aligned with the “do no harm” principle? Is poverty a driver of nature’s decline, or is it the over-consumption that drives environmental degradation? This paper was a great opportunity to question my own views on these very complex ideas and to appreciate the wide diversity of thought going on across the world of conservation.
Fisher, J.A., Dhungana, H., Duffy, J., He, J., Inturias, M., Lehmann, I., Martin, A., Mwayafu, D.M., Rodríguez, I. and Schneider, H. (2020). Conservationists’ perspectives on poverty: An empirical study. People and Nature, 2 (3), pp.678-692.

Chosen by Fionn Ó Marcaigh
Read the full Nature Communications paper here.
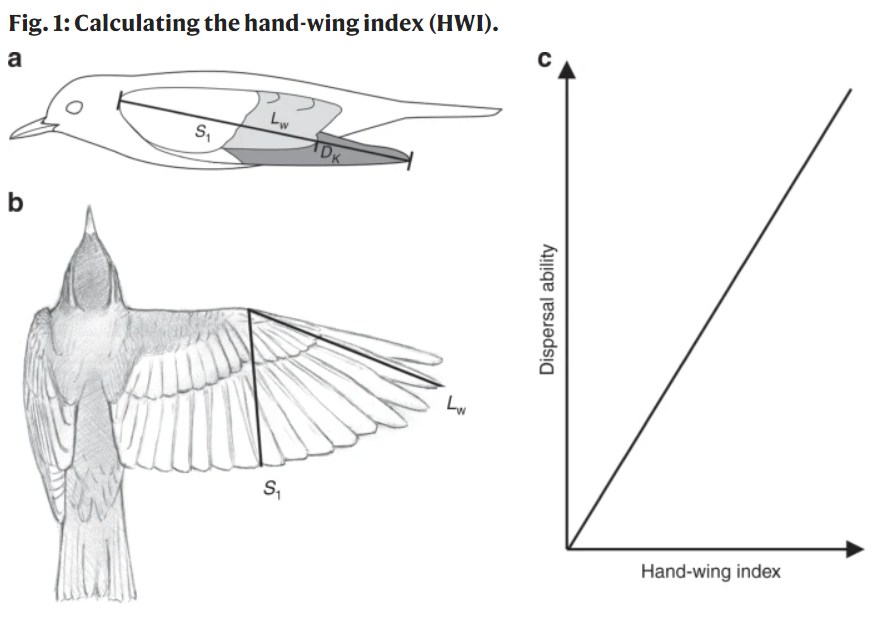
This paper is based on a truly colossal undertaking: to collect their data on dispersal ability, Sheard et al. measured the wings of 10,338 bird species, i.e. 99% of all bird species on Earth. They used the Hand-Wing Index, a measure that correlates with aspect ratio and basically tells you how long and pointed the bird’s wing is. The higher this number (i.e. the pointier the wing), the better the bird will be at dispersing and flying long distances.
© The Author(s) 2020. This article is distributed under the terms of the CC BY 4 license.
This is important for evolution, as the more birds that are able to fly between distant populations the more gene flow there will be and the less likely the populations are to diverge. Sheard et al. found important links between dispersal ability and geography and ecology, as tropical and territorial birds, had lower Hand-Wing Indices and migratory species had higher ones. It’s fascinating to see how these traits affect the ability of a species to move around, which in turn dictates where that species will be found in the world. The authors have made this incredible dataset freely available and it is sure to inform new insights into bird ecology and evolution for years to come.
Sheard C., Neate-Clegg M. H. C., Alioravainen N., Jones S. E. I., Vincent C., MacGregor H. E. A., Bregman T. P., Claramunt S. & Tobias J. A. (2020) Ecological drivers of global gradients in avian dispersal inferred from wing morphology. Nature Communications, 11 (2463).

Chosen by Sam Ross
Read the full Science paper here.
The COVID-19 pandemic has been extremely challenging for many, so it was great to see some excellent science coming from the ‘natural experiment’ offered by COVID-19 movement restrictions. The authors show that during the COVID-19 restrictions anthropogenic noise (from vehicles etc.) in the San Francisco Bay Area reached a 70-year low, characteristic of the mid-1950s. They use a long-term dataset of White-Crowned Sparrow recordings to show that during the COVID-19 lockdown, when human noise pollution was minimal, Sparrows exploited the emptied acoustic space (usually occupied by human-related noise) by producing higher-performance songs at lower amplitudes, to maximise song distance. The authors highlight the rapidity with which behavioural traits (song characteristics) adapted to changes in human activity, suggesting incredible plasticity and potential resilience to pervasive anthropogenic pressures like noise pollution. To me, this study is a perfect example of nature’s resilience, and also on finding opportunity from tragedy (research made possible by a global pandemic).
Derryberry E.P., Phillips J.N., Derryberry G.E., Blum M.J., Luther D. (2020). Singing in a silent spring: Birds respond to a half-century soundscape reversion during the COVID-19 shutdown. Science, 370, 575-579.

Chosen by Jenny Bortoluzzi
Read the full Marine Policy paper here.
This paper looked at the human behavioural responses to a blanket ban on thresher shark fisheries in Sri Lanka and fisher’s perceptions of different aspects of the ban. A blanket ban means a complete prohibition on exploitation of a species, and Thresher sharks are considered to be the most vulnerable species of pelagic sharks. A blanket ban might therefore seem like a straightforward and easy conservation measure to protect them. But this study looked at the human impact behind such a drastic policy decision. A ban like this has consequences for the livelihoods of fishers – particularly smaller fishermen who rely highly on thresher shark landings to provide for their families. The study clearly shows the disparity in the impact this conservation policy has had between fishers who rely on these catches to survive and those for whom they are not the primary catch.
The biggest message I took from this paper is how important it is that human lives are taken into account when making conservation decisions; and more importantly that scientists and policymakers need to involve communities early on in the process, communicate better and work together, not against each other if we want conservation to be effective – and supported. This is a message I think more scientists need to hear and integrate into their work and one I hope to take forward in my future career.
Collins C., Letessier T. B., Broderick A., Wijesundara I., Nuno A. (2020). Using perceptions to examine human responses to blanket bans: The case of the thresher shark landing-ban in Sri Lanka. Marine Policy, 121 (104198).

